Making our streets 'complete'
Complete Streets are streets for everyone. They are designed and operated to enable safe access for all users in a community.
Complete Streets are streets for everyone. They are designed and operated to enable safe access for all users in a community. When creating Complete Streets, priorities need to be balanced between a variety of demands including traffic operations, public safety and health, social equity, and quality of life.
Complete Streets can be applied as a standalone project to improve transportation facilities along a street, or as a network-based approach, allowing for greater flexibility in the application of Complete Streets principles in places where some users may not be adequately accommodated.
For instance, a single street may not be able to accommodate the needs of all users due to constrained space available within the public right-of-way. However, considering the street as part of a network may help identify parallel routes where a different balance of transportation modes can be used to achieve wider network efficiency.
The transportation facilities of different streets then work together as a larger network to provide safe and efficient trips for all modes. Complete Street networks are all-inclusive, making them comfortable and welcoming for everyone, including children, seniors, and people with disabilities.
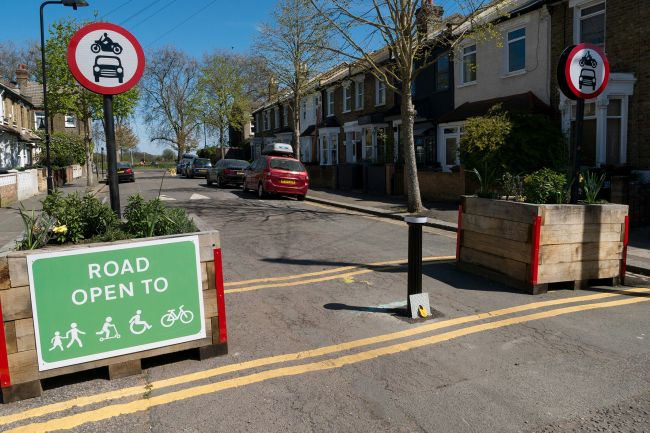
Every street within a Complete Street network looks different, according its role, its context, and the needs and desires of the community it serves. What it takes to make a street “complete” varies depending on many factors, so there is no single definition. However, ingredients may include sidewalks, bike lanes, special bus lanes, comfortable and accessible transit stops, parking and loading zones, frequent crossing opportunities, median islands, accessible pedestrian signals, curb extensions, and more.
All streets are multi-functional spaces; a street may be a key route for people traveling to work and for goods vehicles to deliver to local businesses, while also being a destination for local people to do their shopping, to meet friends, or to attend a school. All these functions can be broadly grouped into two categories: ‘movement’ or ‘place’.
‘Movement’ is about moving people or goods, by various modes of transportation. Streets have a wide range of movement functions, from roads carrying very high volumes and mixes of automobile traffic or people across the region, to streets which provide access to residents in the local neighborhood. Movement includes pedestrians, bicyclists, buses, and other modes, and roads that perform a strategic role must also consider and accommodate these other users.
‘Place’ relates to functions which attract people to walk or spend time in areas adjacent to the street; these functions are equally important to movement. Indeed it is ‘place’ that gives our communities character, amenity, and purpose and, ultimately, makes them livable, desirable places to spend time. Place captures all of the street functions and has a strong relationship with context, particularly land uses and the activity generated by surrounding buildings.
As part of the Orange County Complete Streets Initiative, Steer Davies Gleave is working with the Orange County Council of Governments to show how different types of streets can be classified according to how ‘local’ or ‘strategic’ they are in terms of movement and place functions, and taking into account the mix and balance of transportation modes, the nature of the built environment/aesthetic quality, and the character of different places.
The aim is to enable jurisdictions, agencies, communities, and other stakeholders to:
- identify user needs in different circumstances and set priorities or make trade-offs accordingly when designing Complete Streets;
- reflect changing functions and aspirations as streets change over time;
- balance locally specific needs with the overall function of transportation networks, recognizing that needs may not be the same along the entire length of a street corridor; and
- identify the types of design elements that may be appropriate in a particular context, and with regard to the overall function of the street network.
Find out more about our work in Orange County
Written by Peter Piet.